1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
| import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error, r2_score
# 假设df是包含日期索引和'收盘价'列的DataFrame
# 创建目标变量:下一日收盘价
df['Next_Close'] = df['收盘价'].shift(-1)
df = df.dropna() # 删除最后一行NaN
# 设置滚动窗口大小(250个交易日≈1年)
WINDOW_SIZE = 250
# 初始化存储预测结果的列表
predictions = []
actuals = []
dates = []
# 滚动时间序列交叉验证
for i in range(WINDOW_SIZE, len(df)):
# 获取训练数据(窗口内的前WINDOW_SIZE个点)
X_train = df['收盘价'].iloc[i-WINDOW_SIZE:i-1].values.reshape(-1, 1) # 前一日收盘价
y_train = df['Next_Close'].iloc[i-WINDOW_SIZE:i-1] # 当日收盘价
# 获取测试数据(窗口外的下一个点)
X_test = df['收盘价'].iloc[i-1].reshape(1, -1) # 最后一天的收盘价
y_test = df['Next_Close'].iloc[i] # 要预测的下一天收盘价
# 创建并训练线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测下一个时间点的收盘价
pred = model.predict(X_test)[0]
# 存储结果
predictions.append(pred)
actuals.append(y_test)
dates.append(df.index[i]) # 预测对应的日期
# 转换为DataFrame便于处理
results = pd.DataFrame({
'Date': dates,
'Actual': actuals,
'Predicted': predictions
}).set_index('Date')
# 计算评估指标
mse = mean_squared_error(results['Actual'], results['Predicted'])
rmse = np.sqrt(mse)
mae = mean_absolute_error(results['Actual'], results['Predicted'])
r2 = r2_score(results['Actual'], results['Predicted'])
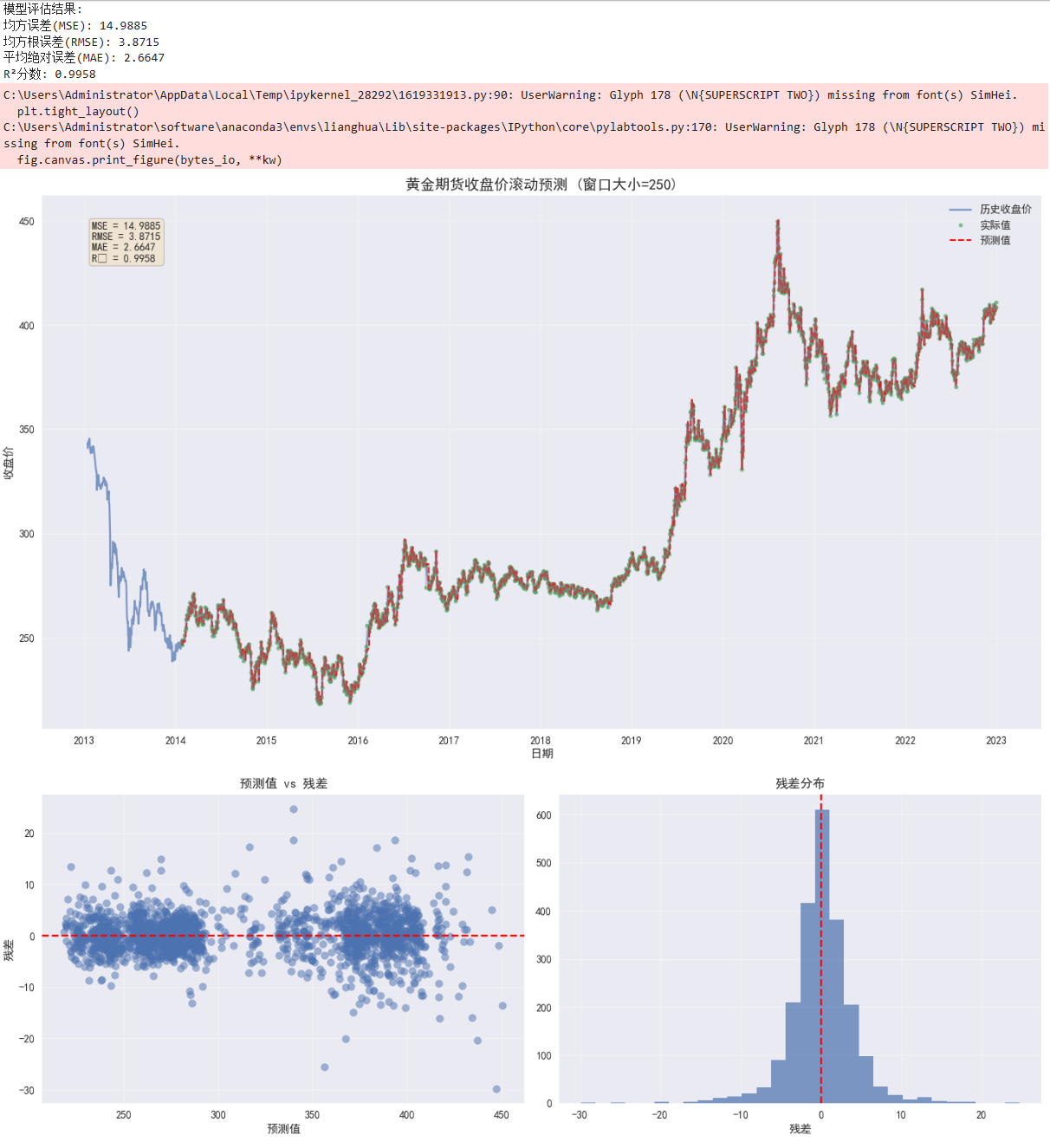
print(f"模型评估结果:")
print(f"均方误差(MSE): {mse:.4f}")
print(f"均方根误差(RMSE): {rmse:.4f}")
print(f"平均绝对误差(MAE): {mae:.4f}")
print(f"R²分数: {r2:.4f}")
# 可视化结果
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 8))
plt.plot(df['收盘价'], label='历史收盘价', alpha=0.7)
plt.plot(results.index, results['Actual'], 'o', label='实际值', markersize=4, alpha=0.7)
plt.plot(results.index, results['Predicted'], 'r--', label='预测值', linewidth=1.5)
# 添加预测误差线
for i, date in enumerate(results.index):
plt.plot([date, date],
[results['Actual'].iloc[i], results['Predicted'].iloc[i]],
'gray', alpha=0.3)
# 添加图例和标题
plt.title(f'黄金期货收盘价滚动预测 (窗口大小={WINDOW_SIZE})', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('日期')
plt.ylabel('收盘价')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
# 添加评估指标文本框
textstr = '\n'.join((
f'MSE = {mse:.4f}',
f'RMSE = {rmse:.4f}',
f'MAE = {mae:.4f}',
f'R² = {r2:.4f}'))
props = dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='wheat', alpha=0.5)
plt.gca().text(0.05, 0.95, textstr, transform=plt.gca().transAxes,
fontsize=10, verticalalignment='top', bbox=props)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 残差分析
residuals = results['Actual'] - results['Predicted']
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.scatter(results['Predicted'], residuals, alpha=0.5)
plt.axhline(y=0, color='r', linestyle='--')
plt.title('预测值 vs 残差')
plt.xlabel('预测值')
plt.ylabel('残差')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.hist(residuals, bins=30, alpha=0.7)
plt.title('残差分布')
plt.xlabel('残差')
plt.axvline(x=0, color='r', linestyle='--')
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
|