1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
| import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import talib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_percentage_error, mean_squared_error
from tqdm import tqdm
# =====================
# 1. 特征工程(参考[1][7][8])
# =====================
def create_features(df, target_col='收盘价'):
"""
创建技术指标和滞后特征
参数:
df: 包含日期索引和收盘价的DataFrame
target_col: 价格列名
返回:
添加新特征的DataFrame
"""
# 基础价格特征
for lag in [1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10]:
df[f'Lag_{lag}'] = df[target_col].shift(lag)
# 技术指标(参考[1][7])
df['MA5'] = talib.SMA(df[target_col], timeperiod=5)
df['MA20'] = talib.SMA(df[target_col], timeperiod=20)
df['RSI'] = talib.RSI(df[target_col], timeperiod=14)
df['MACD'], df['MACD_Signal'], _ = talib.MACD(df[target_col])
# 波动率特征(参考[8])
df['Volatility_5'] = df[target_col].rolling(5).std()
df['Volatility_20'] = df[target_col].rolling(20).std()
# 价格变化特征
df['Price_Change'] = df[target_col].pct_change() * 100 # 百分比变化
# 目标变量:次日收盘价(参考[1])
df['Target'] = df[target_col].shift(-1)
return df.dropna()
# 假设df是包含日期索引和'收盘价'的DataFrame
# 应用特征工程
df = create_features(df.copy())
# =====================
# 2. 滚动时间序列交叉验证(参考[9][11])
# =====================
WINDOW_SIZE = 250 # 使用1年交易日作为滚动窗口(约250天)
features = df.drop(['Target', '收盘价'], axis=1).columns.tolist()
predictions = []
actuals = []
dates = []
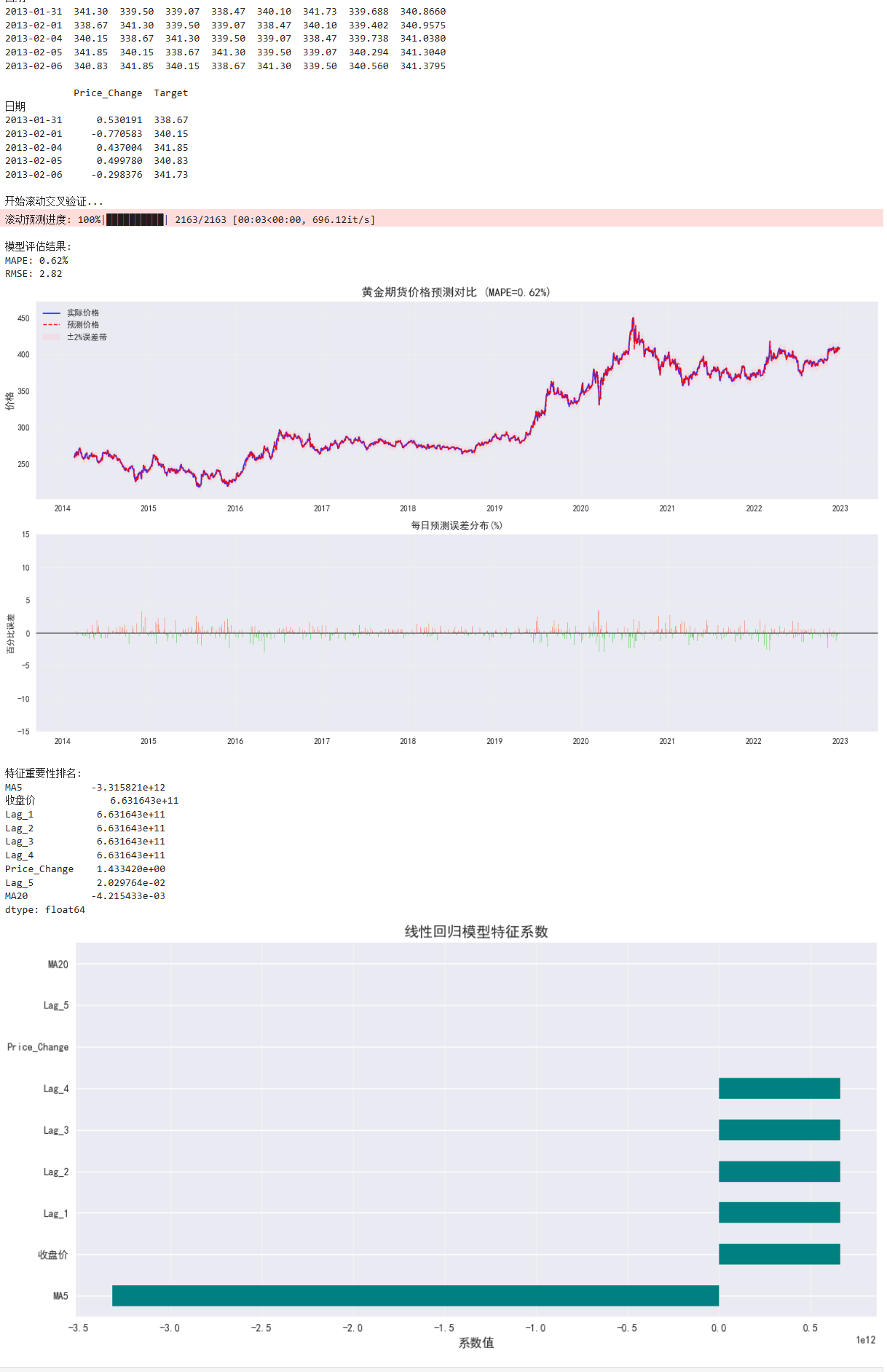
print("开始滚动交叉验证...")
for i in tqdm(range(WINDOW_SIZE, len(df)), desc="滚动验证进度"):
# 划分训练集和测试集(严格按时间顺序)
train = df.iloc[i-WINDOW_SIZE:i-1] # 窗口内除最后一天
test = df.iloc[i-1:i] # 最后一天用于预测次日价格
# 准备数据
X_train = train[features]
y_train = train['Target']
X_test = test[features]
y_actual = df.iloc[i]['Target'] # 实际值(下一天的价格)
# 创建并训练线性回归模型(参考[10])
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测并存储结果
pred = model.predict(X_test)[0]
predictions.append(pred)
actuals.append(y_actual)
dates.append(df.index[i])
# 转换为DataFrame
results = pd.DataFrame({
'Date': dates,
'Actual': actuals,
'Predicted': predictions
}).set_index('Date')
# =====================
# 3. 评估指标计算(参考[1][7])
# =====================
def safe_mape(actual, pred):
"""处理零值的MAPE计算"""
actual = np.array(actual)
pred = np.array(pred)
mask = actual != 0 # 避免除零错误
return np.mean(np.abs((actual[mask] - pred[mask]) / actual[mask])) * 100
mape = safe_mape(results['Actual'], results['Predicted'])
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(results['Actual'], results['Predicted']))
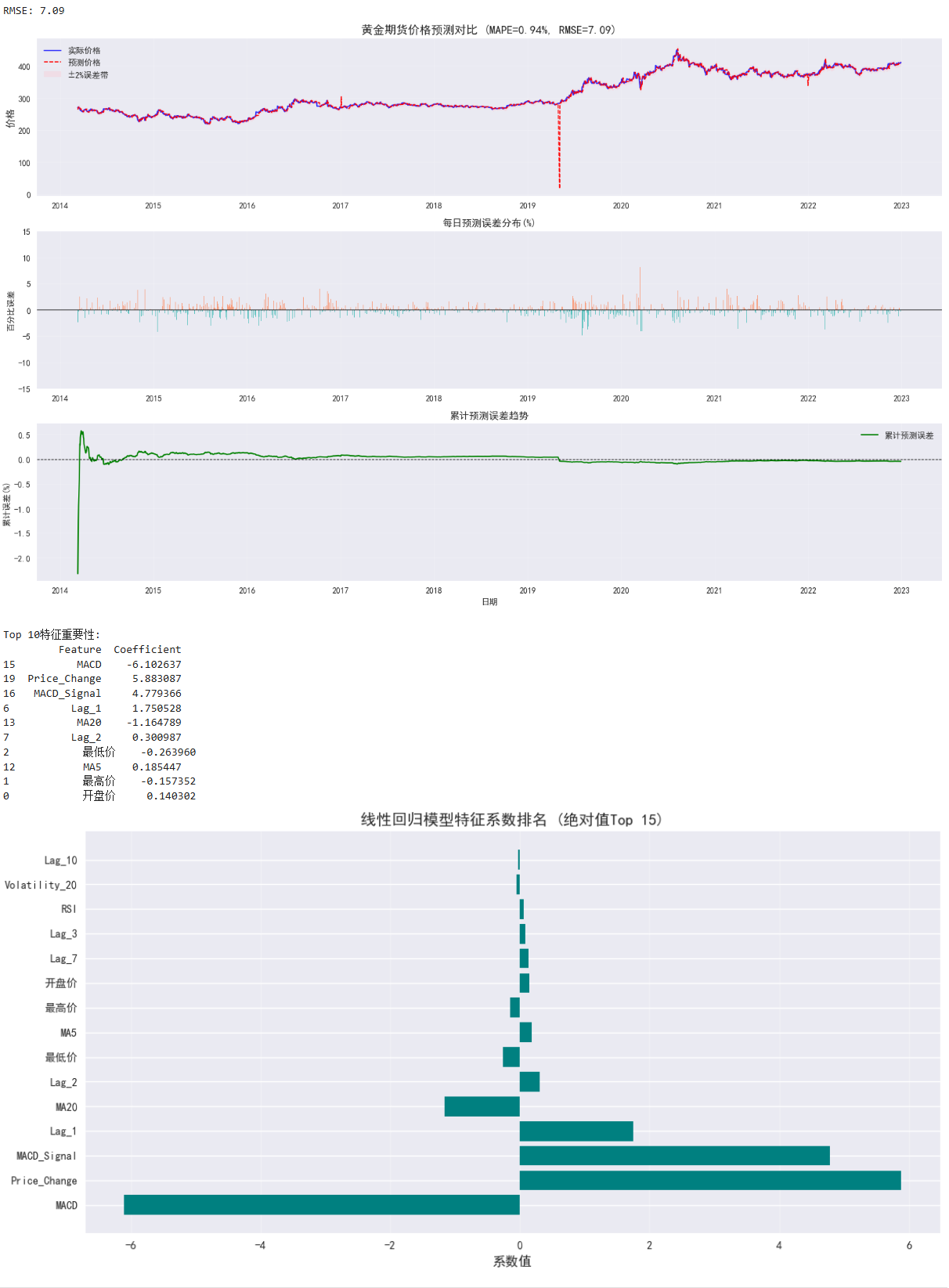
print("\n模型评估结果:")
print(f"MAPE: {mape:.2f}%")
print(f"RMSE: {rmse:.2f}")
# =====================
# 4. 可视化分析(参考[1][5])
# =====================
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 10))
# 1. 主价格曲线对比
plt.subplot(3, 1, 1)
plt.plot(results.index, results['Actual'], 'b-', label='实际价格', alpha=0.8, lw=1.5)
plt.plot(results.index, results['Predicted'], 'r--', label='预测价格', lw=1.2)
plt.fill_between(
results.index,
results['Predicted'] * 0.98,
results['Predicted'] * 1.02,
color='pink', alpha=0.3, label='±2%误差带'
)
plt.title(f'黄金期货价格预测对比 (MAPE={mape:.2f}%, RMSE={rmse:.2f})', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('价格', fontsize=12)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.grid(alpha=0.2)
# 2. 误差分布(百分比误差)
plt.subplot(3, 1, 2)
errors = (results['Predicted'] - results['Actual']) / results['Actual'] * 100
plt.bar(results.index, errors, color=np.where(errors >= 0, 'coral', 'lightseagreen'), alpha=0.7, width=0.8)
plt.axhline(0, color='black', linestyle='-', lw=0.8)
plt.title('每日预测误差分布(%)', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('百分比误差', fontsize=10)
plt.ylim(-15, 15) # 限制误差范围以便观察
plt.grid(alpha=0.2)
# 3. 累计误差分析
plt.subplot(3, 1, 3)
cumulative_error = (results['Predicted'].cumsum() - results['Actual'].cumsum()) / results['Actual'].cumsum() * 100
plt.plot(cumulative_error, 'g-', label='累计预测误差', lw=1.5)
plt.axhline(0, color='black', linestyle='--', lw=0.8)
plt.title('累计预测误差趋势', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('累计误差(%)', fontsize=10)
plt.xlabel('日期', fontsize=10)
plt.grid(alpha=0.2)
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('gold_price_forecast.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
# =====================
# 5. 模型系数分析(参考[10])
# =====================
# 使用最后一次训练的模型分析特征重要性
coef_df = pd.DataFrame({
'Feature': features,
'Coefficient': model.coef_
}).sort_values('Coefficient', key=abs, ascending=False)
print("\nTop 10特征重要性:")
print(coef_df.head(10))
# 可视化特征系数
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
plt.barh(coef_df['Feature'][:15], coef_df['Coefficient'][:15], color='teal')
plt.title('线性回归模型特征系数排名 (绝对值Top 15)', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('系数值', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(axis='x', alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
|