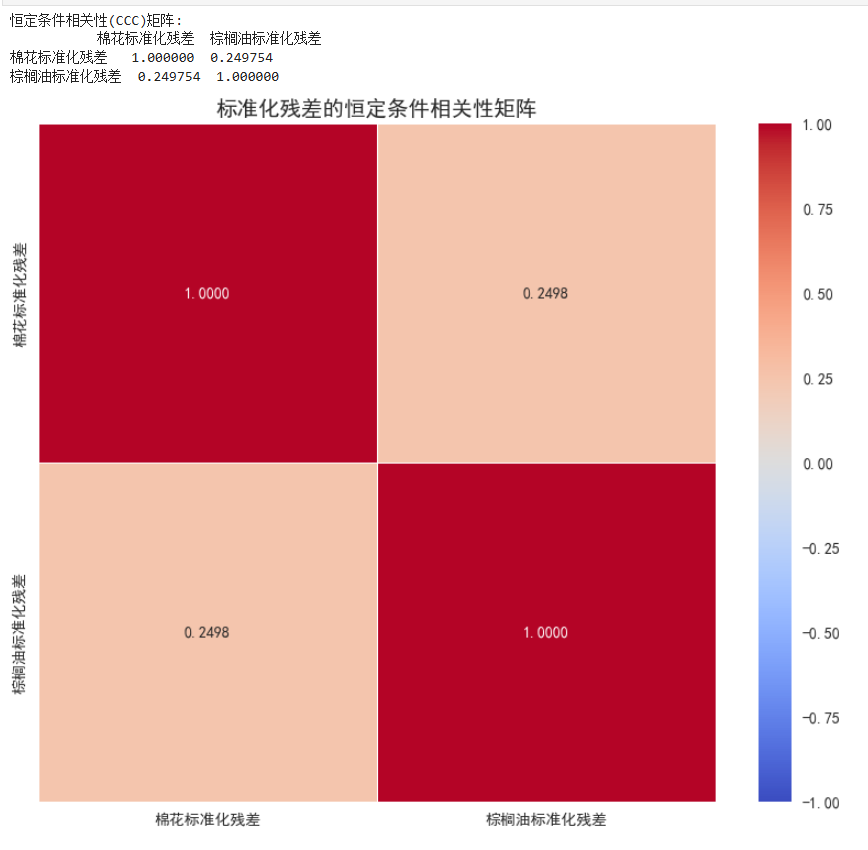
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
| import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from arch import arch_model
# 1. 数据准备(已加载returns DataFrame)
# 假设returns DataFrame包含'棉花期货涨跌'和'棕榈油期货涨跌'两列收益率数据
print(returns.head())
# 2. 初始化存储结果的列表
model_params = [] # 存储模型系数
cond_volatility = [] # 存储条件波动性
std_residuals = [] # 存储标准化残差
garch_models = [] # 存储模型对象本身
model_summaries = [] # 存储模型摘要
forecast_results = [] # 存储预测结果
# 3. 对每个期货品种拟合GARCH模型
commodities = ['棉花期货涨跌', '棕榈油期货涨跌']
for commodity in commodities:
print(f"\n{'='*50}")
print(f"拟合{commodity}的GARCH模型...")
print('='*50)
# 3.1 拟合GARCH(1,1)模型[1,5,10](@ref)
model = arch_model(
returns[commodity].dropna(),
mean='Constant', # 常数均值模型
vol='Garch', # GARCH波动率模型
p=1, # GARCH阶数
q=1, # ARCH阶数
dist='StudentsT' # 使用学生t分布考虑厚尾特征[4](@ref)
)
# 3.2 模型拟合[2,6](@ref)
result = model.fit(disp='off', show_warning=False)
# 3.3 保存模型对象
garch_models.append(result)
# 3.4 保存模型系数[1,10](@ref)
params = result.params
model_params.append(params)
print(f"{commodity}模型参数:")
print(params.to_string())
# 3.5 保存条件波动性[1,7](@ref)
vol_series = result.conditional_volatility
cond_volatility.append(vol_series)
print(f"\n{commodity}平均条件波动率: {vol_series.mean():.4f}")
# 3.6 计算并保存标准化残差[7,8](@ref)
resid = result.resid
std_resid = resid / vol_series
std_residuals.append(std_resid)
print(f"{commodity}标准化残差均值: {std_resid.mean():.4f},标准差: {std_resid.std():.4f}")
# 3.7 保存模型摘要
model_summaries.append(result.summary())
# 3.8 波动率预测(未来5天)[1](@ref)
forecast = result.forecast(horizon=5)
forecast_results.append(forecast)
print(f"\n{commodity}未来波动率预测:")
print(np.sqrt(forecast.variance.iloc[-1]))
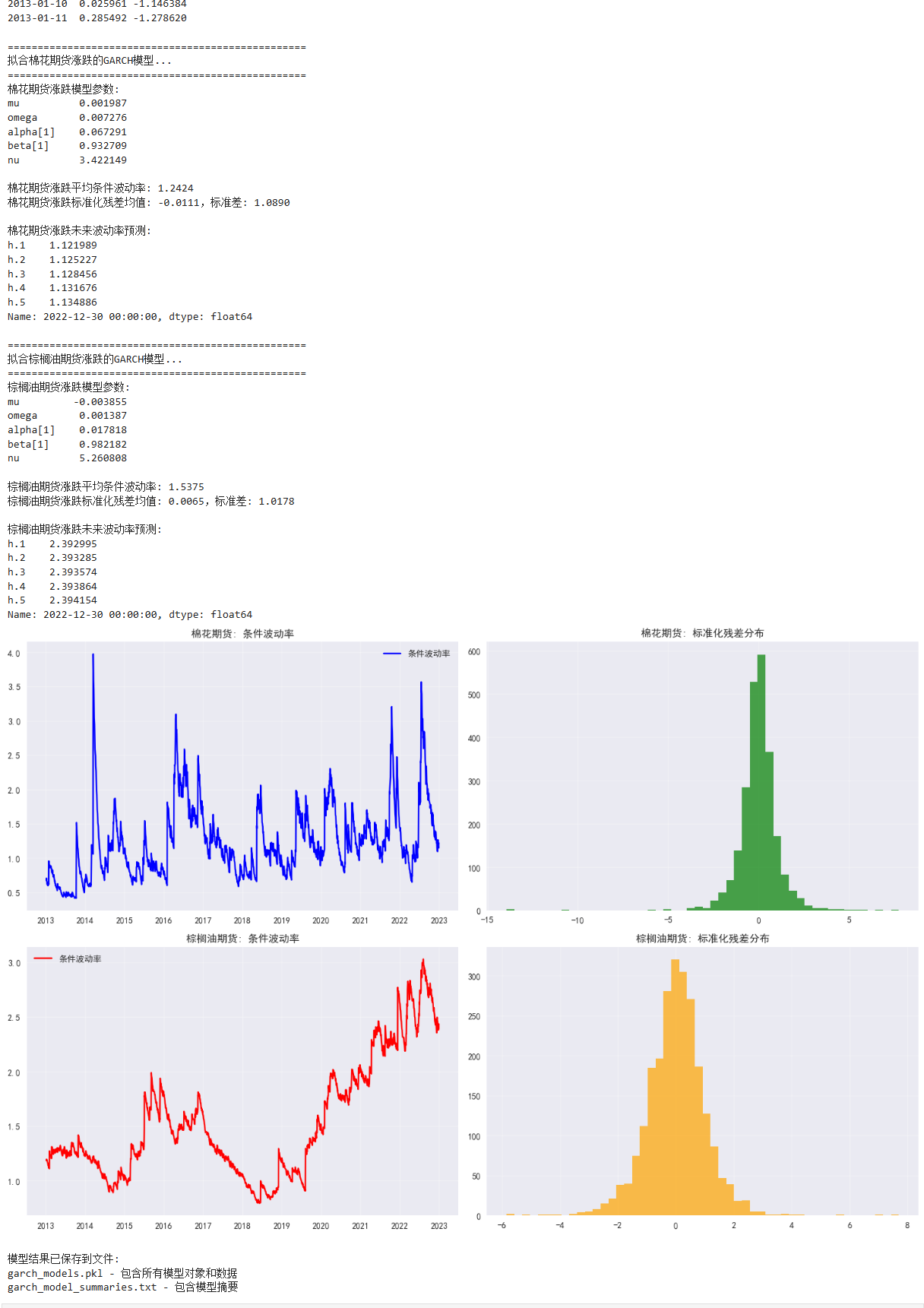
# 4. 结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
# 4.1 棉花期货结果
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.plot(cond_volatility[0], label='条件波动率', color='blue')
plt.title('棉花期货: 条件波动率', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.hist(std_residuals[0], bins=50, alpha=0.7, color='green')
plt.title('棉花期货: 标准化残差分布', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
# 4.2 棕榈油期货结果
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.plot(cond_volatility[1], label='条件波动率', color='red')
plt.title('棕榈油期货: 条件波动率', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.legend()
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.hist(std_residuals[1], bins=50, alpha=0.7, color='orange')
plt.title('棕榈油期货: 标准化残差分布', fontsize=12)
plt.grid(alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('garch_model_results.png', dpi=300)
plt.show()
# 5. 模型保存(可选)[3](@ref)
import joblib
# 5.1 保存模型对象
model_data = {
'commodities': commodities,
'params': model_params,
'cond_volatility': cond_volatility,
'std_residuals': std_residuals,
'models': garch_models
}
joblib.dump(model_data, 'garch_models.pkl')
# 5.2 保存模型摘要文本
with open('garch_model_summaries.txt', 'w') as f:
for i, summary in enumerate(model_summaries):
f.write(f"{'='*50}\n")
f.write(f"{commodities[i]} GARCH模型摘要\n")
f.write(f"{'='*50}\n\n")
f.write(str(summary))
f.write("\n\n\n")
print("\n模型结果已保存到文件:")
print("garch_models.pkl - 包含所有模型对象和数据")
print("garch_model_summaries.txt - 包含模型摘要")
|